Knee effusion is a condition where the amount of fluid in the knee joint increases abnormally, causing the knee to swell, become painful, and restrict movement. This condition often occurs after injury or due to chronic diseases such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
If left untreated, prolonged accumulation of synovial fluid can damage the articular cartilage, impairing mobility and even leading to the risk of losing the ability to walk.
The knee joint capsule is composed of two layers that surround the entire joint surface. The outer layer is responsible for transmitting stimuli from the knee joint to the brain, while the inner layer produces synovial fluid to nourish the articular cartilage and acts as a "shock absorber".
When the synovial membrane is damaged or irritated by external factors, the amount of fluid secreted increases, leading to joint effusion. If not controlled early and properly, this excess fluid can seriously affect the patient's mobility.
Causes of knee joint effusion
Fluid buildup in the knee joint can stem from a variety of causes, similar to effusion in other joints throughout the body. Some common causes include:
Injuries, collisions
The knee joint is subjected to significant pressure during strenuous activity, excessive sports performance, or accidents at work or in daily life, which can lead to meniscal tears, fractures, ligament ruptures (anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament), cartilage damage, and consequently, effusion.
Arthritis
Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout can all cause inflammation and increase joint fluid production.
Joint infection
Bacteria invade the joint, causing an inflammatory response and fluid buildup. Common causative agents include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus suis, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis; viruses or fungi can also be involved.
Signs of knee joint effusion
Swelling and persistent pain in the knee joint are early warning signs of knee effusion. Visually, the affected knee joint may appear significantly larger than the other.
Patients should seek medical attention promptly if they experience the following symptoms:
- Sharp pain when weight is placed on the leg or when the knee joint is subjected to impact.
- Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, limited range of motion in extending the knees, standing up and sitting down, especially after waking up.
- The skin around the knee joint is red and feels hot to the touch.
- Bruising and bleeding in cases of injury.
While knee effusion is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact daily life. If left untreated, the swelling and pain will worsen and may lead to complications such as:
- Joint stiffness, joint fusion, joint deformity.
- Misalignment of limbs, osteoarthritis.
- Joint infections, osteoporosis around the joints.
Therefore, when symptoms such as pain and swelling appear, especially signs of infection or injury, patients need to seek medical attention early. In cases where there is swelling and redness of the joint accompanied by fever, loss of sensation in the knee area, or inability to move or walk independently, immediate emergency care is required.
Even if joint swelling is not accompanied by the dangerous symptoms mentioned above, patients should still seek medical attention early to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
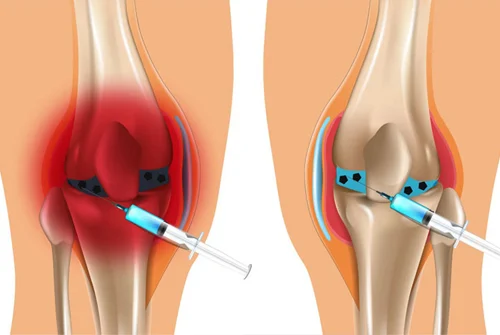
Knee effusion is a condition in which the amount of fluid in the knee joint increases abnormally.
Diagnosis of knee joint effusion
To accurately diagnose knee effusion, doctors rely not only on clinical symptoms but also order tests and paraclinical methods to determine the cause and extent of the damage.
- Blood tests: These help detect signs of inflammation, infection, or related conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout.
- Diagnostic imaging: X-rays assess the condition of bones and joints, detecting fractures, dislocations, bone tumors, or degeneration; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of soft tissues around the joint such as ligaments, tendons, menisci, and articular cartilage.
- Joint fluid aspiration: Joint fluid is extracted for analysis to detect inflammation, infection, or abnormal crystals such as urate crystals in gout.
Treatment of knee joint effusion
Treatment for knee effusion depends on the cause, extent of damage, and specific symptoms. Methods may be applied individually or in combination.
- Medical treatment
Suitable for mild cases of effusion with a clearly identified cause. Commonly used medications include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anti-edema medications. This method is effective in conditions such as gout, osteoarthritis of the knee, and rheumatoid arthritis. Patients must strictly follow their doctor's instructions and not change the dosage or stop medication on their own.
- Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is indicated when effusion is accompanied by complex injuries such as meniscal tears, ligament ruptures, or chronic capsular inflammation. Arthroscopy allows the surgeon to directly observe the inside of the joint to excise and suture the meniscus, clean the joint, or reconstruct the ligaments. This method also aids in diagnosis and biopsy in difficult cases.
- Joint fluid aspiration
This procedure is used when a large amount of fluid causes pain and restricts movement. The doctor uses a specialized needle to drain the fluid to reduce pressure in the joint, and may combine this with injections or antibiotics depending on the case.
In summary: Knee joint effusion is not always a medical emergency; however, patients should pay particular attention to dangerous warning signs such as high fever, swelling, redness, burning sensation, severe pain, loss of mobility, or inability to stand steadily. These could be signs of joint infection or serious injury, requiring prompt medical intervention.
Even without acute symptoms, persistent knee swelling and pain of unknown origin is a valid reason to seek medical attention. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment will help limit complications and shorten recovery time.
